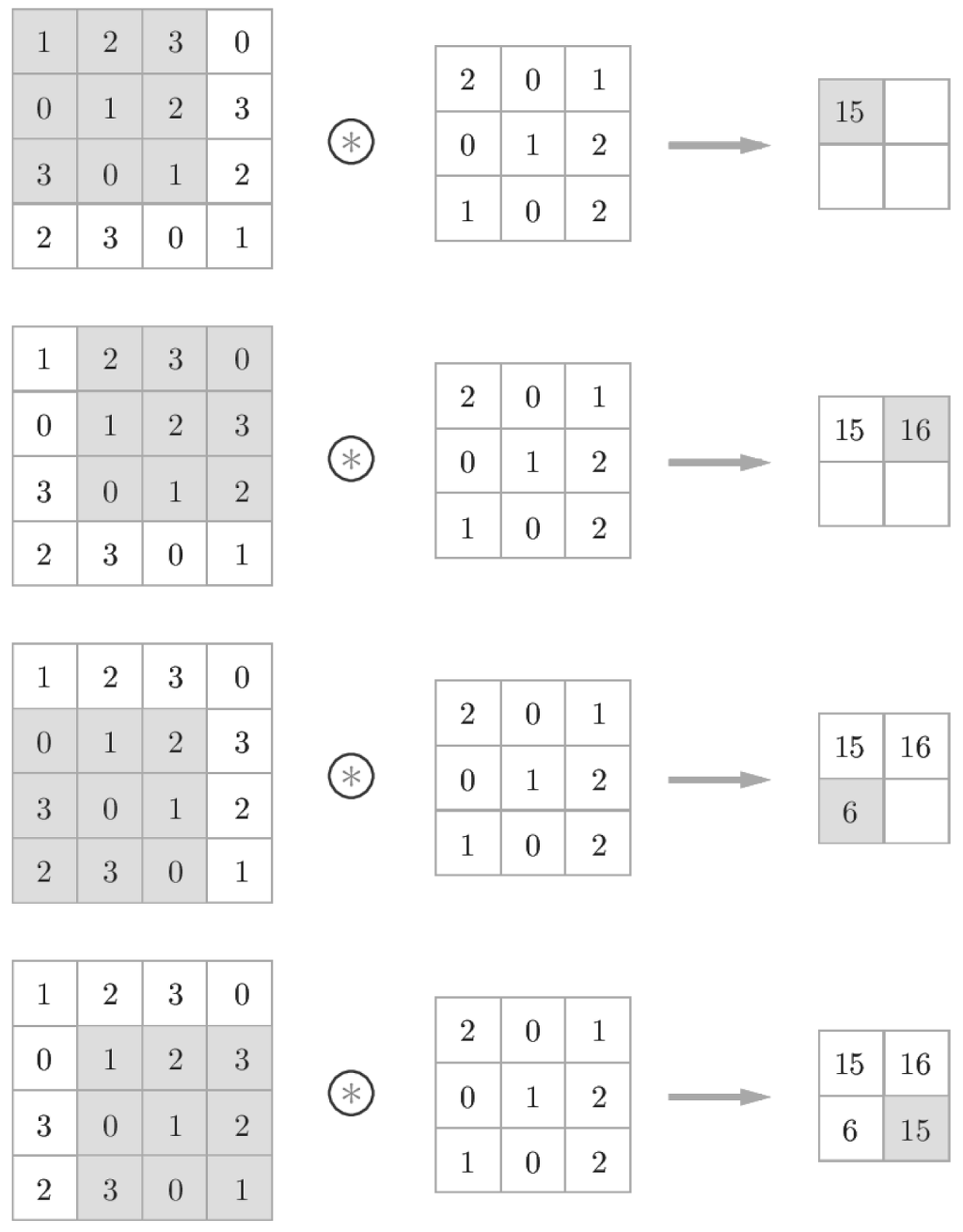
위의 이미지에서 맨 마지막 연산이 15가 되도록 하는 파이썬 코드
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
import numpy as np
x = np.array([[1,2,3,],[0,1,2],[3,0,1]])
filter = np.array([[2,0,1],[0,1,2],[1,0,2]])
print(np.sum(x*filter)) # 15
|
cs |
covolution 과정을 이해하기 위한 빌드업 문제와 코드

|
1
2
3
|
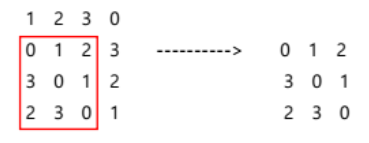
a = np.array([[1,2,3,0],[0,1,2,3],[3,0,1,2],[2,3,0,1]])
print(a[0:3,0:3])
|
cs |

|
1
|
print(a[1:4,0:3])
|
cs |

import numpy as np
# data array인 a와 filter array인 filter를 생성한다.
a = np.array([[1,2,3,0],[0,1,2,3],[3,0,1,2],[2,3,0,1]])
filter = np.array([2,0,1,1]).reshape(2,2)
# matrix_convolution 함수
def matrix_convolution (data,filter_data,stride) :
# stirde * (filter_data[열] or filter_data[행])이 data의 열, 혹은 행보다 크면 안됨
if stride*filter_data.shape[0] > data.shape[0] or stride*filter_data.shape[1] > data.shape[1] :
return 'stride가 너무 큽니다.'
# 결과 리스트 생성, 결과를 담을 행렬의 shape을 위해서 count_i, count_j 만듦
result = []
count_i = 0
count_j = 0
# convolution 코드
for i in range(0,data.shape[0]-filter_data.shape[0]+1,stride) :
count_i += 1
for j in range(0,data.shape[1]-filter_data.shape[1]+1,stride) :
count_j += 1
result.append(np.sum(data[i:filter_data.shape[0]+i,j:filter_data.shape[1]+j]*filter_data))
# 결과 list를 count_i와 count_j를 이용하여 배열로 생성
result = np.array(result).reshape(int(count_j/count_i),count_i)
return result
matrix_convolution(a,filter,2)
'코딩 > 문제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 문제6. (파이썬) 합병정렬 (0) | 2020.06.05 |
|---|---|
| 문제5. (파이썬) 삽입정렬 (0) | 2020.06.04 |
| 문제4. (파이썬) 버블정렬 (0) | 2020.06.03 |
| 문제3. (파이썬) 이진탐색 (0) | 2020.06.02 |
| 문제1. (파이썬) np.dot을 for문으로 구현하기 (0) | 2020.05.15 |